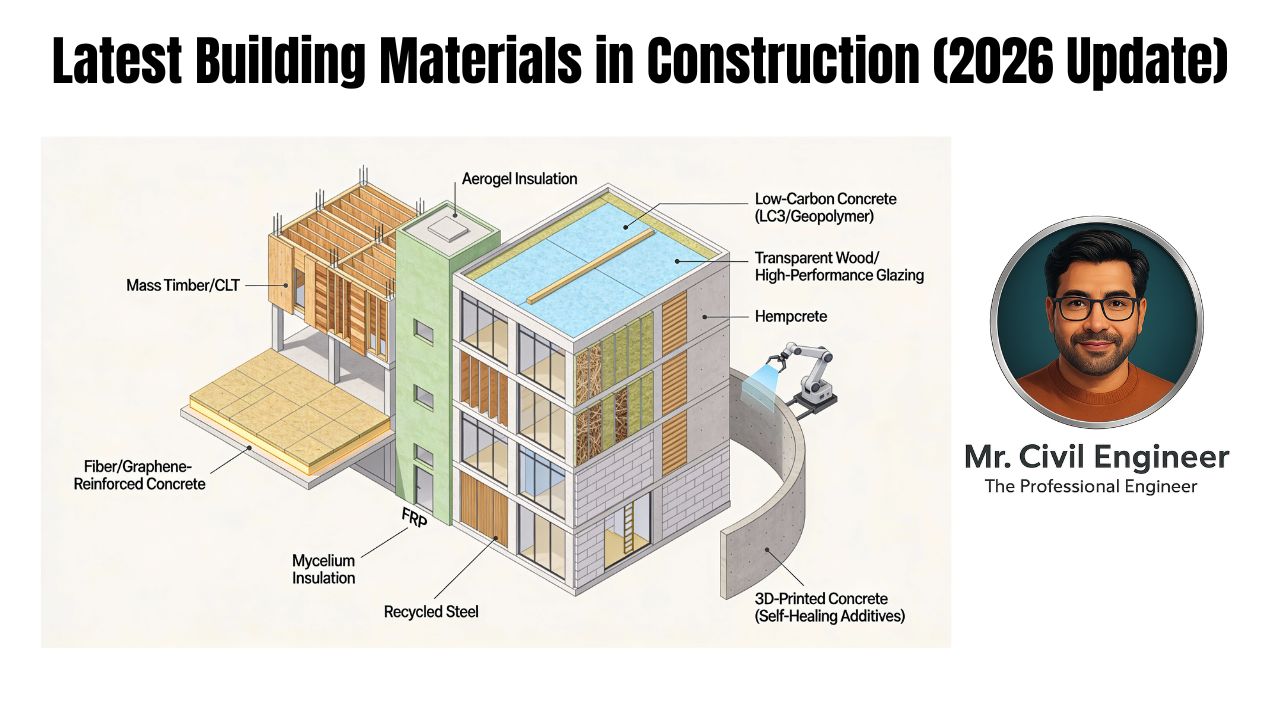
Cement production pumps out 8% of global CO2—more than aviation and shipping combined. Yet 2026 brings game-changers: materials that capture carbon, self-repair cracks, or grow from fungi, slashing emissions while delivering skyscraper strength. If you’re speccing for India’s booming infra, these latest building materials in construction make sustainability practical.
This 2026 update spotlights top innovations—greener, smarter, tougher—with real-world uses, costs, and tips. From PMAY housing to green towers, here’s what to watch.
Sustainable Concrete Innovations
Concrete evolves beyond Portland cement.
Carbon-Capturing Concrete
Binds CO2 during curing via mineralization.
- Features: Reduces net emissions 40–50%; M30+ strength.
- Uses: Urban slabs, pavements. India example: Pilot in Delhi Metro expansions.
Self-Healing Concrete
Bacteria/polymers seal cracks autonomously.
- Benefits: 50% less maintenance; 200-year lifespan potential.
- Cost: 20–30% premium, dropping fast.
Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC)
Nano-silica/quartz for 150–250 MPa strength.
- Uses: Thin bridges, retrofits. Stat: 10x thinner than normal concrete.
Geopolymer Concrete
Fly ash/slag activated alkali—no clinker.
- Green win: 80% lower CO2. India: Slag-rich from steel plants.
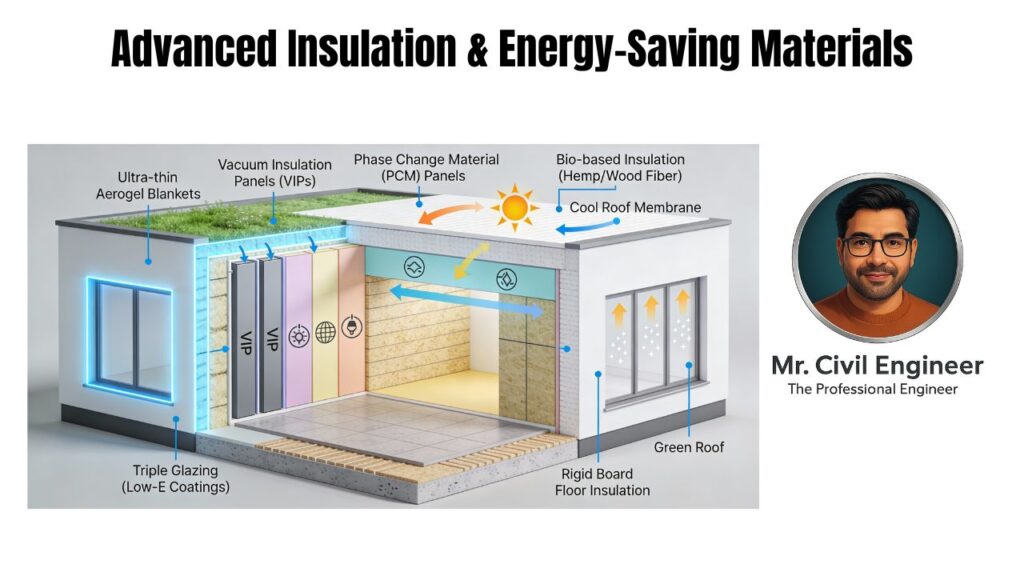
Advanced Insulation & Energy-Saving Materials
Efficiency meets extreme performance.
Aerogel Insulation
Silica nano-foam, R-value 10x traditional.
- Features: 3–10mm thick, fireproof, hydrophobic.
- Uses: Walls/roofs in hot climates. Cost: ₹4000–6000/m² but pays back in 3 years via AC savings.
Phase-Change Materials (PCM)
Microcapsules absorb/release heat (e.g., paraffin in walls).
- Benefits: Stabilizes indoor temps 5–8°C. Trend: Plasterboard-integrated for homes.
Vacuum-Insulated Panels (VIPs)
Glass fiber in vacuum, R-40 per inch.
- Uses: Prefab modules, cold storage.
Timber & Bio-Based Revolution
Renewables rise.
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
Glued wood layers, concrete-like strength.
- Features: Fire-resistant, seismic-flexible; 8-story buildings possible.
- India: Bamboo-CLT hybrids for Northeast projects. Cost: ₹2500–4000/m².
Mycelium Bricks
Fungi-grown blocks from waste.
- Green: Carbon-negative, biodegradable. Uses: Non-load-bearing partitions. 2026 pilots: Eco-villages.
Engineered Bamboo
Laminated boards rival steel.
- Strength: Tensile 200 MPa. Local: Abundant, fast-growing.
High-Performance Composites
Next-gen durability.
Graphene-Enhanced Materials
Carbon sheets boost concrete/steel 2–3x.
- Features: Crack-proof, conductive (self-heating roads). Cost: ₹1000/kg additive.
Recycled Plastic Aggregates
PET/plastic waste replaces 20–100% gravel.
- Benefits: Lighter (20% less dead load), leachate-resistant. India: Swachh Bharat tie-ins.
Translucent Wood
Delignified timber, polymer-infused for light transmission.
- Uses: Aesthetic facades, daylighting. Cool factor: Glows naturally.
Smart & Functional Materials
Tech-embedded.
Self-Cleaning Coatings
TiO2 nano-layers break down dirt/viruses via UV.
- Uses: Facades, reducing cleaning 70%.
Shape-Memory Alloys (SMA)
Nitinol wires “remember” shape, auto-repair cracks.
- Future: Earthquake retrofits.
| Material | Sustainability | Strength Gain | India Cost (₹/m²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-Capturing Concrete | High (40% CO2 cut) | Normal | 500–800 |
| Aerogel Insulation | High | N/A | 4000–6000 |
| CLT Timber | High | High | 2500–4000 |
| Geopolymer Concrete | Very High | Normal | 400–600 |
| Mycelium Bricks | Highest | Low | 200–400 (pilots) |
2026 Adoption Guide for India
- Residential: Geopolymer + recycled plastics (PMAY green push).
- Commercial: UHPC + aerogels for towers.
- Trends: 30% material cost drop via local sourcing; govt incentives for low-carbon certs.
Pro tip: Test small pilots; integrate with BIM for specs.
Challenges: Supply chains scaling (e.g., graphene imports), but 2026 sees 25% adoption growth.
FAQs
Cheapest latest building material?
Recycled plastic aggregates (~₹300/m³ savings).
Most sustainable?
Mycelium bricks or geopolymer (80–100% CO2 cut).
Available in India now?
Yes: UHPC, aerogels via UltraTech/Asian Paints; CLT emerging.
Conclusion
The latest building materials in construction for 2026 aren’t gimmicks—they’re tools for net-zero, resilient builds amid climate pressures. From carbon-eating concrete to fungi bricks, pick based on your project’s needs, budget, and green goals.
Stay updated via IGBC webinars, source locally, and lead the shift. Your next site could pioneer India’s sustainable future.
Read This Also
How to Calculate Building Cost Before Construction: Your Step-by-Step Guide
How to Estimate Brickwork and Rate Analysis with Example
Artificial Intelligence in Civil Engineering: How Smart Infrastructure is Being Built
Advanced Materials for Civil Engineering: Trends & Applications