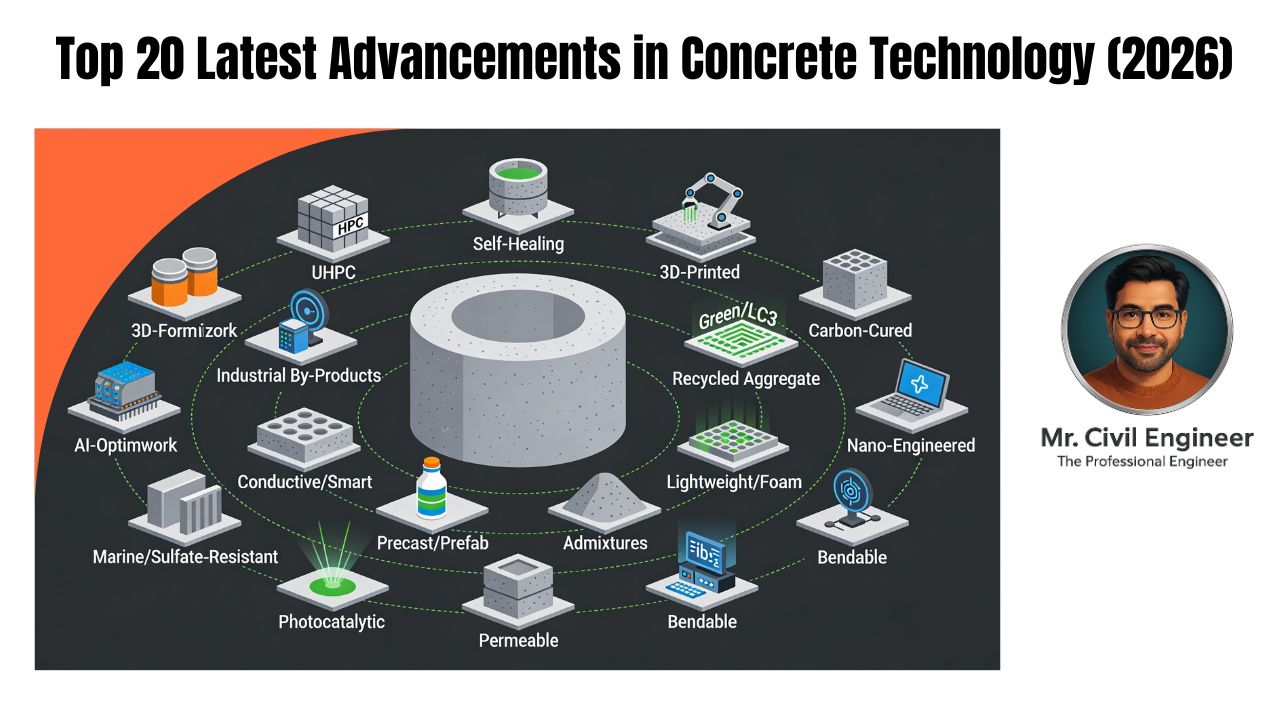
Concrete has supported civilization’s grandest structures—from the Roman aqueducts to today’s towering skyscrapers. But as demands rise for sustainability, durability, and smart infrastructure, traditional concrete evolves rapidly. The latest advancements in concrete technology are pushing boundaries, offering stronger, greener, and longer-lasting materials that are transforming construction globally.
This article explores the top 20 concrete tech breakthroughs reshaping the industry in 2025 and beyond, helping engineers, builders, and developers stay ahead with practical innovations.
Smart and Sensor-Embedded Concrete
Smart concrete embeds tiny sensors and IoT devices within the material matrix. These sensors monitor parameters like temperature, humidity, strain, and crack formation in real time. This data enables predictive maintenance—spotting structural issues before failures happen—greatly enhancing safety and reducing costly repairs.
Field tests have shown smart concrete prolongs infrastructure life and improves asset management, key for bridges, tunnels, and high-rise buildings.
3D Printed Concrete
3D printing concrete layer-by-layer allows architects and engineers to realize complex shapes previously impossible or cost-prohibitive. The process reduces material wastage and speeds construction timelines, making it ideal for bespoke facade elements, structural components, and repairs.
Pilot projects in marine and urban environments demonstrate enhanced flexibility and rapid prototyping with this method.
Self-Healing Concrete
Self-healing concrete uses bacteria or encapsulated chemicals that activate when microscopic cracks form, releasing limestone or healing agents that seal cracks autonomously. This reduces maintenance cycles and significantly extends structural lifespan.
Variants can last up to 200 years in harsh exposure environments, proven in marine piers and tunnels.
Green and Sustainable Concrete
Sustainability drives concrete innovation with use of recycled industrial byproducts like fly ash, slag, and novel lignocellulose admixtures. Carbon-absorbing concretes chemically sequester CO2, reducing net emissions during the curing process. Programs by research labs focus on low-carbon alternatives to Portland cement without compromising strength.
Green concretes improve environmental footprints while meeting evolving building codes.
Nano-Enhanced and Graphene Concrete
Nanomaterials incorporated into concrete enhance microstructure for superior strength, durability, and rapid early gain. Graphene-enhanced mixes show reductions in clinker content but reach around 78 MPa compressive strength at 28 days in pilot slabs, promising a leap in performance.
Commercial adoption is growing cautiously due to costs and supply logistics.
Engineered Cementitious Composites (Bendable Concrete)
Bendable or ECC concretes introduce fibers and tailor mix designs to impart flexibility and ductility, significantly mitigating brittle cracking. These materials are gaining traction in seismic zones and infrastructure requiring enhanced toughness.
Pervious and Lightweight Concrete
Pervious (or permeable) concretes allow water infiltration, reducing drainage issues and urban flooding risks. Lightweight concretes reduce structural load and improve thermal insulation, aiding energy-efficient construction.
Advanced Additives and Densifiers
Recent concrete densifiers cure faster and offer self-leveling properties, improving finishing quality and durability. New formulations are eco-friendlier and reduce VOC emissions, supporting green building certifications.
Other Emerging Trends
- Carbon-neutral cements and mineralization processes.
- Digital, automated batching plants with data-driven quality control.
FAQs
What is self-healing concrete?
A concrete that repairs cracks autonomously using embedded bacteria or chemicals, reducing maintenance needs.
How does 3D printed concrete help construction?
Allows creation of complex, bespoke shapes faster with minimal waste, improving design freedom and efficiency.
Are graphene-enhanced concretes widely used?
Early-stage commercial projects exist, but cost and dispersion challenges slow widespread adoption.
What does “green concrete” mean?
Concretes made with recycled materials or CO2 capture features to lower environmental impact.
Conclusion
Concrete technology is evolving at an unprecedented pace. From smart sensing to carbon-absorbing mixes and 3D printing, these advancements promise safer, longer-lasting, and greener buildings. Adopting innovative concrete solutions today equips the construction industry to meet tomorrow’s infrastructure challenges sustainably and efficiently.