Introduction
Imagine a city where traffic lights adapt to real-time traffic flow, garbage bins notify authorities when they’re full, and your home adjusts its temperature based on your habits. This is the promise of IoT (Internet of Things) infrastructure in smart cities. As urban populations continue to grow, the need for efficient, sustainable, and safe urban management has never been greater. This article will delve into how IoT is revolutionizing cities and what that means for urban planning and development.
What is IoT Infrastructure?
At its core, IoT infrastructure refers to the network of sensors, devices, and systems that collect and exchange data in real time. In a smart city, IoT infrastructure connects everything from streetlights to waste bins, making urban management more efficient and dynamic. IoT devices can range from small sensors embedded in roads to large-scale systems for managing traffic, energy, and water.
Key components include:
- Sensors: Devices that collect data (temperature, traffic flow, waste levels).
- Data Networks: The means through which data travels (cellular, Wi-Fi, 5G).
- Cloud-based Platforms: Centralized hubs for storing, processing, and analyzing data.
Benefits of IoT in Smart Cities
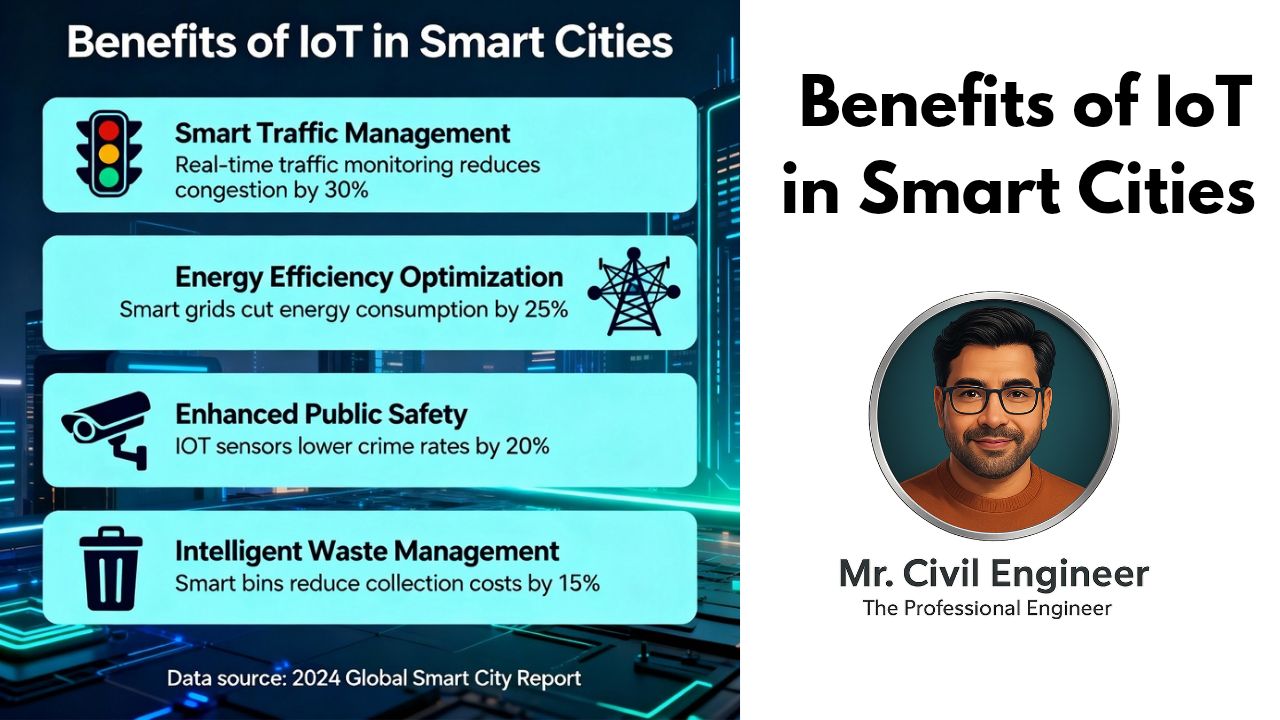
1. Improved Efficiency:
From reducing energy consumption to optimizing traffic flow, IoT infrastructure enables cities to use resources more effectively. For instance, smart traffic lights can adjust to real-time traffic patterns, reducing congestion and fuel consumption.
2. Enhanced Sustainability:
IoT can monitor air quality, water usage, and energy consumption, ensuring that cities remain environmentally friendly. Cities like Copenhagen use IoT to track energy usage and improve waste management, reducing their carbon footprint.
3. Public Safety:
Smart cities use IoT to enhance public safety through surveillance systems, predictive policing, and emergency response optimization. Singapore uses IoT to integrate surveillance with real-time crime data, improving its ability to respond to emergencies.
4. Quality of Life:
With smart homes, public spaces, and transportation systems powered by IoT, cities are becoming more livable. Barcelona, for example, has smart street lighting that adjusts based on pedestrian movement, saving energy while improving safety.
Real-World Applications of IoT in Cities
- Smart Traffic Management (Singapore):
IoT-powered traffic management systems help alleviate congestion by adjusting traffic lights based on real-time traffic data. The result? Faster commutes and reduced emissions. - Smart Waste Management (New York City):
IoT sensors in trash bins alert waste management teams when bins are full, ensuring efficient pickups and reducing unnecessary trips. - Smart Buildings and Energy Efficiency (Los Angeles):
Energy-efficient smart buildings equipped with IoT sensors adjust heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy, saving both energy and costs.
Challenges in Implementing IoT in Cities
While IoT offers tremendous benefits, cost and data security remain significant challenges. Implementing large-scale IoT systems requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology. Moreover, protecting citizens’ data privacy in a connected urban environment is crucial, especially as cities collect vast amounts of personal data.

The Future of Smart Cities and IoT
With the rise of 5G and edge computing, IoT infrastructure will become more powerful, faster, and efficient. The integration of autonomous vehicles, AI, and big data will further shape the future of smart cities, driving innovation in urban management and enhancing residents’ quality of life.
Conclusion
Smart cities powered by IoT are no longer a futuristic concept—they’re already here. As IoT technologies evolve, cities around the world will become smarter, more sustainable, and more livable. Whether you’re a city planner, tech enthusiast, or business owner, understanding the potential of IoT in urban infrastructure is essential for shaping the future of cities.
FAQs
- What is the primary function of IoT in smart cities?
IoT helps cities optimize resources, improve services, and enhance sustainability through interconnected devices and sensors. - How can IoT improve traffic management?
IoT uses real-time data to adjust traffic lights and manage congestion, reducing travel time and emissions. - What are the security risks associated with IoT in cities?
IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, which poses risks related to privacy and cybersecurity. Strong encryption and data protection measures are critical. - How can IoT help in waste management?
Sensors in waste bins monitor fill levels and alert authorities for timely pickups, reducing inefficiencies and improving urban cleanliness.
Read This Also
How to Calculate Building Cost Before Construction: Your Step-by-Step Guide
Building Information Modeling (BIM) and 4D/5D BIM: The 2025 Guide
Artificial Intelligence in Civil Engineering: How Smart Infrastructure is Being Built